Gateway API
Learn about Kubernetes Gateway API, the recommended replacement for Ingress Nginx
Gateway API
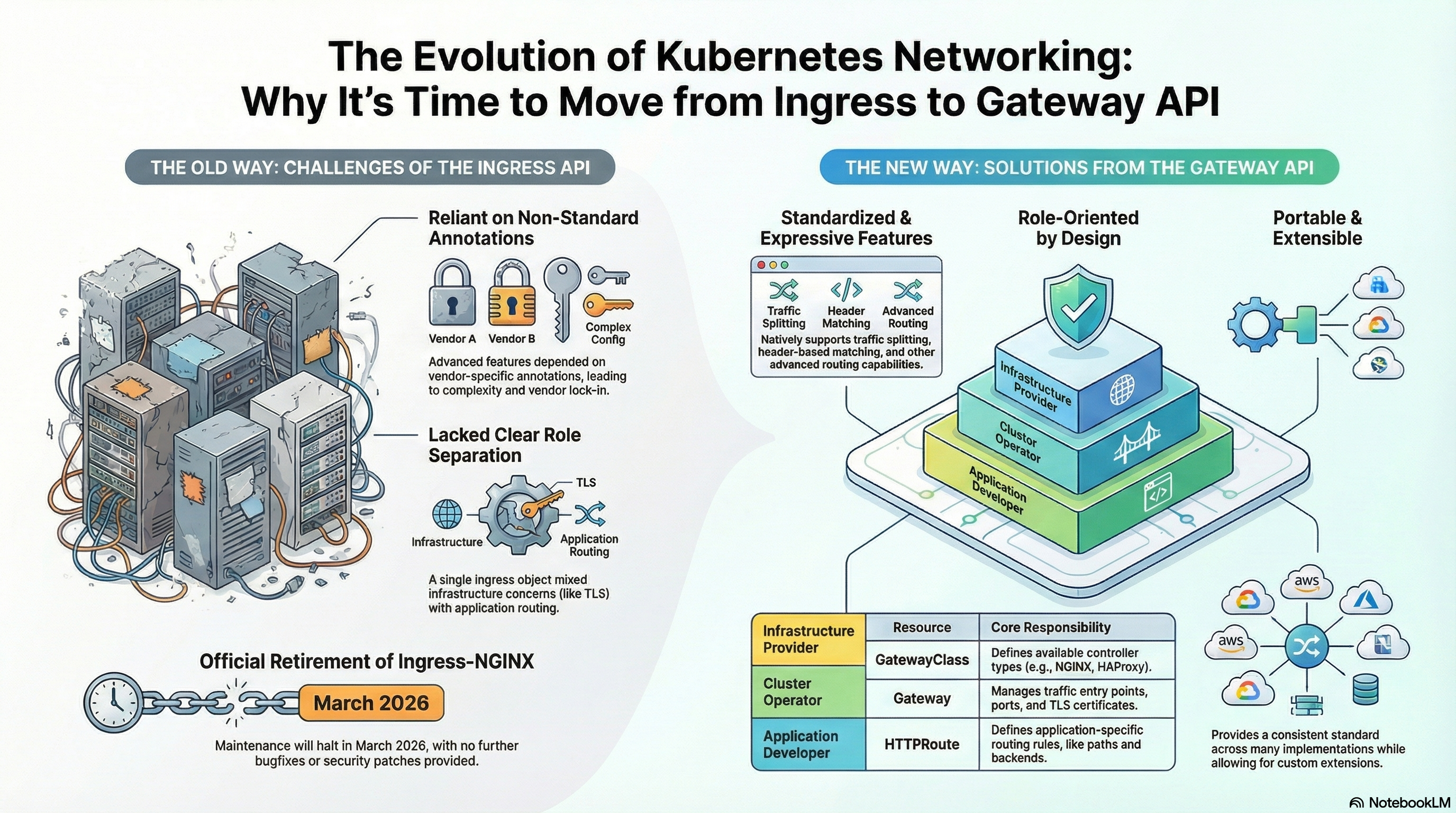
The Kubernetes Gateway API is the recommended replacement for Ingress, providing a more expressive, extensible, and role-oriented approach to managing traffic routing in Kubernetes clusters. It addresses the limitations of the original Ingress resource by introducing protocol-specific routing resources and a layered architecture.
What is the Gateway API?
The Gateway API is a Kubernetes project that provides a standardized way to configure networking in Kubernetes. It moves away from the single, monolithic Ingress object by breaking routing configuration into multiple components, supporting typed Route resources for different protocols.
Key Improvements Over Ingress
- Protocol Support: Native support for multiple protocols (HTTP, TLS, TCP, UDP, gRPC)
- Standardization: Avoids vendor lock-in from controller-specific annotations
- Role-Oriented Design: Separates infrastructure concerns from application routing
- Expressiveness: Advanced features built into the spec, not hidden in annotations
Protocol-Specific Route Resources
The Gateway API routing layer features protocol-specific resources:
- HTTPRoute: For HTTP or terminated HTTPS connections
- TLSRoute: For TLS or HTTPS traffic
- TCPRoute: For TCP traffic
- UDPRoute: For UDP traffic
- GRPCRoute: For gRPC traffic
Addressing Ingress Limitations
Previously, Ingress natively only supported HTTP routing and lacked native support for TCP and UDP routing, which had to be handled by specific controllers. The Gateway API makes these protocol routes standard Kubernetes objects, allowing flexibility in supporting various protocols.
HTTPRoute: Core Component
The HTTPRoute is a central component of the Kubernetes Gateway API, serving as one of the protocol-specific resources that define the behavior of L7 (Layer 7) routing.
Core Functionality
- Traffic Direction: Creates simple rules for directing network traffic to applications
- Matching and Backend References: Uses rules that specify matches (like path prefix matching) and backend references (
backendRefs) to direct traffic - Binding: Specifies connection to a parent
Gatewayresource usingparentRefs, enabling it to consume the infrastructure provided by the Gateway
Example HTTPRoute
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: http-app-route
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
hostnames:
- "example.com"
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /api
backendRefs:
- name: my-service
port: 8080
Advanced Features
The Gateway API supports features that were only possible in Ingress through custom annotations:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Traffic Splitting/Weighted Load Balancing | Allows specifying weights (e.g., 80% to V1 and 20% to V2) for backend services, enabling canary deployments |
| HTTP Redirects and Rewrites | Supports configuring HTTP redirects and URL rewrites |
| Header Modification | Allows modifying HTTP request and response headers |
| CORS Configuration | Cross-Origin Request (CORS) configuration is defined inside the spec section under filters |
| Request Mirroring | Supports configuring Request Mirroring |
Layered Architecture
The Gateway API uses a layered approach to networking concerns:
- Infrastructure Layer (
GatewayClassandGateway): Handles ports, certificates, and controller selection (managed by Cluster Operators) - Routing Layer (
HTTPRoute,TCPRoute, etc.): Handles application-specific routing logic like paths, weights, and headers (managed by Application Developers)
This separation is analogous to having distinct building blueprints: one blueprint (Gateway) handles the foundation, walls, and utilities for a whole apartment complex, while another set of blueprints (HTTPRoute) defines the interior layout, furniture placement, and specific entrance rules for each individual apartment within that complex.
Role-Oriented Design
The Gateway API separates responsibilities:
- Cluster Operators: Manage
GatewayClassandGatewayresources (infrastructure concerns like TLS certificates) - Application Developers: Create and manage protocol-specific routes like
HTTPRoute(application routing logic)
This abstraction allows developers to define traffic rules for their applications without needing to understand infrastructure details.
Standardization and Portability
The Gateway API ensures that configurations are:
- Kubernetes-Aware: Configurations are defined within the
specsection of resources, making Kubernetes aware of them - Vendor-Neutral: Forces underlying products (like NGINX or Traefik) to conform to standards
- Portable: Avoids vendor lock-in caused by controller-specific annotations found in Ingress
Getting Started
Prerequisites: Installing Gateway API CRDs
⚠️ CRITICAL: Install Gateway API CRDs First!
Before applying any Gateway API resources, you MUST install the Gateway API Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) in your Kubernetes cluster. Gateway API resources (GatewayClass, Gateway, HTTPRoute, etc.) are NOT part of standard Kubernetes - they need to be installed as CRDs first. This is the most common mistake!
Option 1: Install from NGINX Gateway Fabric (Recommended if using NGINX)
kubectl kustomize "https://github.com/nginx/nginx-gateway-fabric/config/crd/gateway-api/standard?ref=v2.2.1" | kubectl apply -f -
Option 2: Install from Official Gateway API Repository
kubectl kustomize "https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/releases/download/v2.2.1/standard-install.yaml" | kubectl apply -f -
Verify CRDs are Installed:
kubectl get crd | Select-String gateway
You should see CRDs like:
gatewayclasses.gateway.networking.k8s.iogateways.gateway.networking.k8s.iohttproutes.gateway.networking.k8s.io
Installing a Gateway Implementation
After CRDs are installed, install a Gateway API implementation. For NGINX Gateway Fabric:
helm install ngf oci://ghcr.io/nginx/charts/nginx-gateway-fabric --create-namespace -n nginx-gateway
Wait for the deployment to be ready:
kubectl wait --timeout=5m -n nginx-gateway deployment/ngf-nginx-gateway-fabric --for=condition=Available
Basic Setup Order
- GatewayClass: Defines the controller type (NGINX Gateway Fabric automatically creates one named
nginx) - Gateway: Creates network endpoints (listeners) for traffic - similar to setting up an Ingress Controller
- HTTPRoute: Defines routing rules for HTTP/HTTPS traffic - similar to an
Ingressresource
Path Routing
Gateway API supports three types of path matching:
- PathPrefix - Matches any path that starts with the specified prefix (most common)
- Exact - Matches only the exact path specified
- RegularExpression - Matches paths using regular expressions
Path Prefix Matching
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: httproute-path-prefix
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /api
backendRefs:
- name: api-service
port: 8080
Key Points:
- Matches:
/api,/api/,/api/v1,/api/users/123 - Doesn't match:
/apis,/apiary - Use this for routing API endpoints, static file paths, or any hierarchical path structure
Exact Path Matching
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: httproute-path-exact
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: Exact
value: /health
backendRefs:
- name: health-service
port: 8080
Key Points:
- Matches:
/health(exactly) - Doesn't match:
/health/,/health/check,/healthcheck - Use this when you need precise path matching without any sub-paths
Multiple Path Rules
Rules are evaluated in order - first match wins. More specific paths should come before less specific ones:
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: httproute-multiple-paths
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /api/v2
backendRefs:
- name: api-v2-service
port: 8080
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /api
backendRefs:
- name: api-service
port: 8080
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /
backendRefs:
- name: default-service
port: 8080
Header-Based Routing
Gateway API supports native header matching, which is a significant advantage over Nginx Ingress where header-based routing requires custom server snippets.
Basic Header Matching
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: httproute-header-match
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
rules:
- matches:
- headers:
- name: X-Environment
value: staging
backendRefs:
- name: staging-service
port: 8080
- matches:
- headers:
- name: X-Environment
value: production
backendRefs:
- name: production-service
port: 8080
- backendRefs:
- name: default-service
port: 8080
Key Points:
- Header matching is native in Gateway API (no annotations needed)
- Headers are matched exactly by default
- Can combine header matching with path matching
- Default route handles requests without matching headers
Multiple Header Conditions
AND Logic: All headers in a single headers array must match
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: httproute-multiple-headers
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /api
headers:
- name: X-Environment
value: staging
- name: X-User-Type
value: premium
backendRefs:
- name: premium-staging-service
port: 8080
Use Cases:
- Environment routing: Route to staging/production based on headers
- Feature flags: Enable features for specific users or groups
- A/B testing: Route traffic to different service versions
- User segmentation: Route premium users to different backends
Traffic Splitting and Canary Deployments
Gateway API provides native support for traffic splitting, making it much easier than Nginx Ingress which requires multiple resources and annotations.
Weighted Traffic Splitting
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: httproute-weighted
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /
backendRefs:
- name: v1-service
port: 8080
weight: 90
- name: v2-service
port: 8080
weight: 10
Key Points:
- Weights are relative (e.g., 90 + 10 = 100, so 90% and 10%)
- All weights are summed, then each backend receives its proportional share
- Useful for gradual rollouts and A/B testing
- Can split between any number of backends
Canary Deployment Pattern
Progressive canary rollout pattern - adjust weights to gradually increase canary traffic:
- Phase 1: 95/5 (5% canary) - Initial testing
- Phase 2: 90/10 (10% canary) - Increased confidence
- Phase 3: 75/25 (25% canary) - Half traffic
- Phase 4: 50/50 (50% canary) - Complete rollout
- Phase 5: 0/100 (100% canary) - Complete migration
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: httproute-canary
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /
backendRefs:
- name: stable-service
port: 8080
weight: 90
- name: canary-service
port: 8080
weight: 10
Traffic Mirroring
Sends a copy of traffic to a secondary service. The primary service still handles the request and responds normally:
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: httproute-mirror
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /
backendRefs:
- name: primary-service
port: 8080
filters:
- type: RequestMirror
requestMirror:
backendRef:
name: mirror-service
port: 8080
Use Cases:
- Testing new services with production traffic
- Analytics and monitoring
- A/B testing data collection
- Debugging production issues
TLS/SSL Configuration
Unlike Nginx Ingress where TLS is configured per Ingress resource, Gateway API configures TLS at the Gateway level. This provides centralized certificate management and better separation of concerns.
Gateway with TLS Configuration
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: my-gateway
spec:
gatewayClassName: nginx
listeners:
- name: https
protocol: HTTPS
port: 443
hostname: example.com
tls:
mode: Terminate
certificateRefs:
- name: example-tls
Key Points:
- TLS is configured in the Gateway resource, not HTTPRoute
- Certificates are stored in Kubernetes Secrets
- Use
certificateRefsto reference the Secret - TLS mode:
Terminate(most common)
Creating TLS Secrets:
# Manual creation
kubectl create secret tls example-tls \
--cert=path/to/cert.crt \
--key=path/to/cert.key
# Or use cert-manager for automatic certificate management
TLS Termination Flow
Client → HTTPS → Gateway (TLS termination) → HTTP → Backend Service
Key Points:
- TLS is terminated at the Gateway
- Backends receive plain HTTP (port 80)
- Simplifies backend configuration
- Gateway handles all TLS complexity
Note: NGINX Gateway Fabric only supports Terminate mode. TLS passthrough is not supported by NGF.
Filters: Request and Response Modifications
Filters allow you to modify requests before they reach backends and responses before they reach clients. This replaces Nginx Ingress annotations with native, portable filter types.
URL Rewriting
Rewrites request paths before forwarding to backend:
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: httproute-url-rewrite
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /api
filters:
- type: URLRewrite
urlRewrite:
path:
type: ReplacePrefixMatch
replacePrefixMatch: /
backendRefs:
- name: api-service
port: 8080
Common Use Cases:
- Strip
/apiprefix:/api/users→/users - Path migrations:
/old-api→/new-api - Version routing:
/v1/api→/api
Header Modification
Modifies headers before forwarding (request) and before responding (response):
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: httproute-header-modify
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /
filters:
- type: RequestHeaderModifier
requestHeaderModifier:
add:
- name: X-API-Version
value: v2
set:
- name: X-Forwarded-Proto
value: https
remove:
- X-Debug-Header
- type: ResponseHeaderModifier
responseHeaderModifier:
add:
- name: X-Content-Type-Options
value: nosniff
set:
- name: Cache-Control
value: "no-cache, no-store"
backendRefs:
- name: my-service
port: 8080
Operations:
add: Add new headersset: Overwrite existing headersremove: Delete headers
Redirects
Redirects requests to a different URL:
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: httproute-redirect
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /old
filters:
- type: RequestRedirect
requestRedirect:
scheme: https
hostname: new.example.com
path:
type: ReplacePrefixMatch
replacePrefixMatch: /new
statusCode: 301
Common Use Cases:
- HTTP to HTTPS redirects
- Domain migrations
- Path changes
- Temporary redirects for maintenance
Filter Types
- URLRewrite: Rewrite request paths
- RequestHeaderModifier: Modify request headers
- ResponseHeaderModifier: Modify response headers
- RequestRedirect: Redirect requests
- RequestMirror: Mirror traffic
- ExtensionRef: Custom filters (implementation-specific)
Advanced Matching
Gateway API supports sophisticated matching capabilities that allow you to route traffic based on multiple criteria simultaneously.
HTTP Method Matching
Routes traffic based on HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.):
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: httproute-method-match
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /api
method: GET
backendRefs:
- name: read-service
port: 8080
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /api
method: POST
backendRefs:
- name: write-service
port: 8080
Query Parameter Matching
Routes based on URL query parameters:
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: httproute-query-params
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
rules:
- matches:
- queryParams:
- name: version
value: v2
backendRefs:
- name: v2-service
port: 8080
- matches:
- queryParams:
- name: version
value: v1
backendRefs:
- name: v1-service
port: 8080
Common Use Cases:
- API versioning via query params (
?version=v2) - Environment routing (
?env=staging) - Feature flags (
?feature=new-ui)
Complex Matching Logic
AND Logic (within a match block): All conditions in a single match block must be true
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: httproute-multiple-matches
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: my-gateway
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /api
headers:
- name: X-Environment
value: staging
method: POST
queryParams:
- name: version
value: v2
backendRefs:
- name: staging-v2-write-service
port: 8080
OR Logic (multiple match blocks): Any match block can match
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /api
headers:
- name: X-Environment
value: staging
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /api
headers:
- name: X-Environment
value: development
backendRefs:
- name: dev-staging-service
port: 8080
Matching Types Supported:
- Path: PathPrefix, Exact, RegularExpression
- Headers: Exact, RegularExpression
- Query Parameters: Exact, RegularExpression
- HTTP Method: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH, OPTIONS, etc.
- Hostname: Exact match on hostname
Migration from Ingress
Resource Mapping
| Nginx Ingress | Gateway API | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| IngressClass | GatewayClass | Defines controller type |
| Ingress Controller Setup | Gateway | Network endpoints and TLS |
| Ingress Resource | HTTPRoute | Routing rules |
| Ingress TLS | Gateway TLS | Centralized at Gateway level |
| Ingress Backend | BackendRef | More powerful in Gateway API |
Annotation Mapping
| Nginx Annotation | Gateway API Equivalent |
|---|---|
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target | URLRewrite filter |
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-weight | weight in backendRefs |
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/permanent-redirect | RequestRedirect filter |
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/enable-cors | CORSPolicy |
Key Differences
Architecture:
- Nginx Ingress: Single
Ingressresource for all configuration - Gateway API: Separate
Gateway(infrastructure) andHTTPRoute(application)
TLS Configuration:
- Nginx Ingress: TLS configured per Ingress
- Gateway API: TLS configured once at Gateway level
Portability:
- Nginx Ingress: Nginx-specific annotations, not portable
- Gateway API: Standard API, works across implementations (Nginx, Istio, Contour, etc.)
Expressiveness:
- Nginx Ingress: Limited native features, requires annotations
- Gateway API: Native support for advanced routing, rich filter system
Migration Checklist
- Install Gateway API CRDs
- Install Gateway implementation
- Create GatewayClass
- Create Gateway with TLS
- Migrate Ingress to HTTPRoute
- Migrate annotations to filters/policies
- Test routing
- Test TLS
- Test advanced features
- Monitor metrics
- Remove old Ingress resources
Troubleshooting
Error: "no matches for kind 'GatewayClass'"
Problem: Gateway API CRDs are not installed.
Solution: Install CRDs first (see Getting Started section).
Gateway Status Shows "Not Ready"
Possible causes:
- NGINX Gateway Fabric is not installed or not running
- GatewayClass doesn't exist or has wrong controller name
- Network policies blocking traffic
Check:
kubectl get pods -n nginx-gateway
kubectl get gatewayclass
kubectl describe gateway my-gateway
Implementation
The NGINX Gateway Fabric project provides an implementation of the Gateway API using NGINX as the data plane, demonstrating how the Gateway API can be implemented with existing infrastructure components.